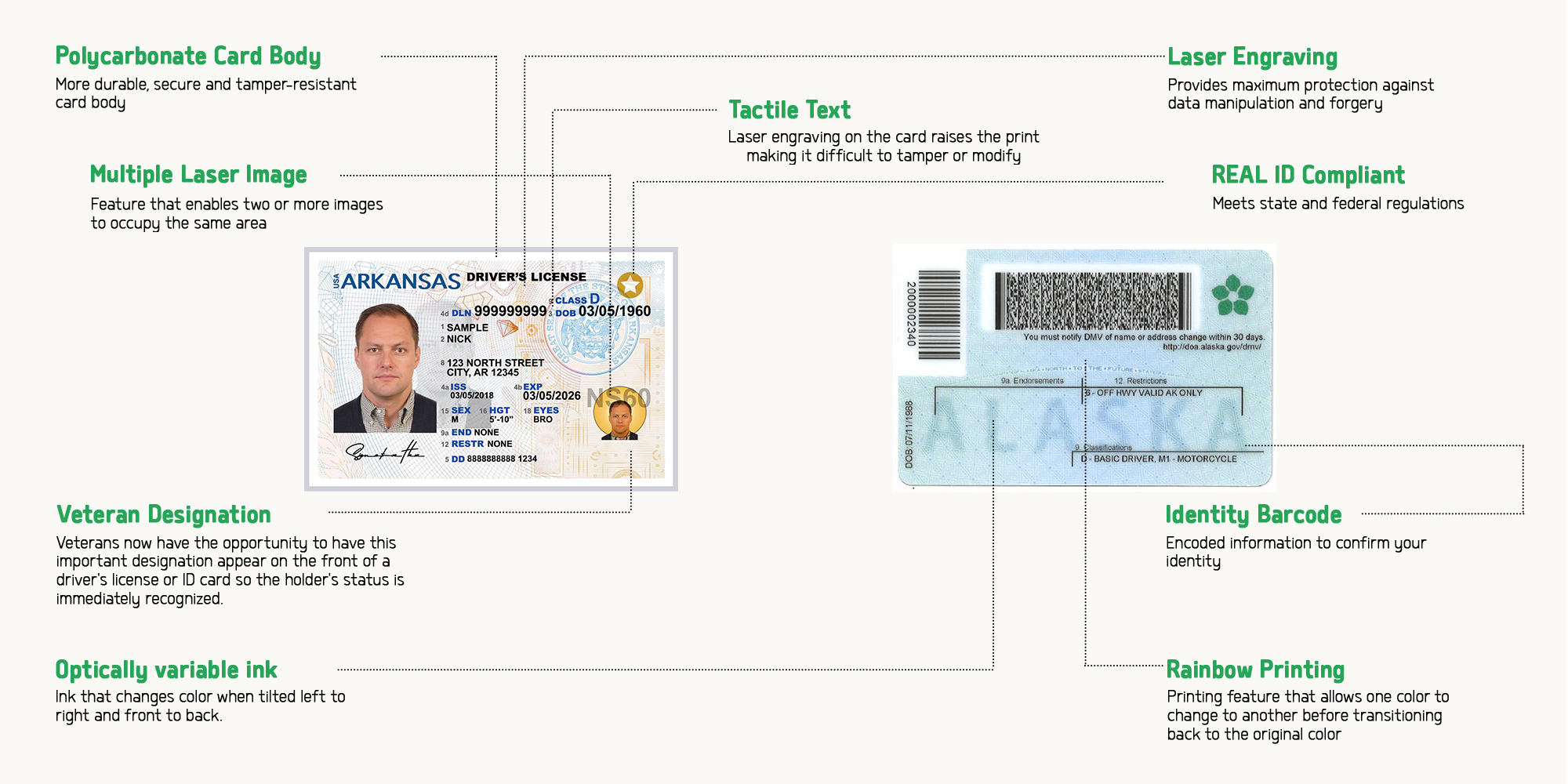

As an ID maker, we take great care to ensure that the driver’s licenses and state-issued ID cards we produce are highly secure and resistant to counterfeiting. One of the key ways we do this is by incorporating a variety of security features into the design of the cards.
We Accept BTC AND GIFT CARD
N.B: WE ALWAYS ENCOURAGE CRYPTO PAYMENT FOR BEING ANONYMOUS.(IF YOU MAKE PAYMENT THROUGH CRYPTO THEN, YOUR INFORMATION WILL BE 100% ANONYMOUS. OTHER FORM OF PAYMENT COULD BE TRACKED BY CYBER SECURITY. EMAIL US (FAKEDL@PROTONMAIL.COM) FOR MORE DETAIL.
Holograms
We use state of the art holographic printing methods to create highly detailed and secure holograms that can display images or text that change when viewed from different angles. These holograms are created using a process called holographic printing, which involves capturing a 3D image of an object and then reproducing it on a flat surface. This makes it extremely difficult for counterfeiters to replicate, and provides an additional layer of security for the license.
Watermarks
To incorporate watermarks, we use specialized printing process that embeds the image or pattern into the card’s substrate. Watermarks are images or patterns that are incorporated into the material of the card and can be seen when held up to the light or viewed at a certain angle. These watermarks are typically made using a specialized printing process that embeds the image or pattern into the card’s substrate. The watermarks are designed to be difficult to replicate. .
Microprinting
We use specialized printing equipment that can print microtext, patterns or other designs which are almost impossible to replicate. Microprinting is a technique that uses very small text that is difficult to replicate and read without magnification. The microprinting is typically added to the design of the license in various areas such as the signature, photograph, or other key elements of the license.
RFID chips
We integrate RFID chips that can be used for electronic verification and can be read by a scanner. These chips contain a unique identification number that can be read by an electronic reader, allowing authorized personnel to quickly and easily verify the authenticity of the license.
UV printing
We include designs, images or text that can only be seen under ultraviolet light. This feature can be used to verify the authenticity of the license by checking for the presence of a hidden image or text that is not visible under normal lighting conditions. .
Barcodes
We include machine-readable barcodes or QR codes that can be scanned to confirm the authenticity of the license. These barcodes can be scanned using a barcode reader or smartphone, and can contain a variety of information such as the holder’s name, date of birth, and license number.
How our Fake ID'S look like
More About Fake Driving License
Scannable High-Quality
We offer you High Quality Scannable Fake id which is exactly like a real one. Each of our IDs comes with High-quality holograms and materials. You can check out Fake id Pictures before placing an order. We are the only ones using Polycarbonate & Teslin to make the ID look identical. No one can spot the differences. So why are you wasting time, order yours and enjoy the party.
Security Measure
We know the purpose of ordering a fake id. So, we consider all security measurements in our ID so that no one can spot the differences. You can easily use our ID at a liquor store, bar, or at the club without having any security issues. We are going to make an identical Fake id for you.
Express Delivery
We know the importance of your Need so we have made a solution to satisfy your need as soon as possible. We can hand over your ID within 2 weeks or less depending on the shipping method you do prefer. However, our standard shipping takes 3-4 weeks to be shipped in your address.
Available Stats
We know your need and purpose. According to your need, we are here to provide you with the best identical fake ids you are expecting within a very short time.






